Breast exam
In this section :
1. Breast exam – what is it?
2. Self-breast Examination – when should you start?
1. Breast exam – what is it?
Clinical breast examinations can detect a lump in your breast and other changes that might require more testing. Breast exams are one of the most important early breast cancer screenings.
A clinical breast examination is done by a trained healthcare provider.
Frequency
- Age 20 to 40 : every 3 years
- After 40 years: Annually
2. Self-breast Examination – when should you start?
Breast self-examination should be conducted once a month by all women starting from 20 years of age.
It is better to conduct a self-breast examination one week after the beginning of menstruation (During menstruation, some women feel their breasts painful and lumpy). If not menstruating, a convenient date can be selected.
Steps of self-breast examination:
- Inspection (Preferably in standing position)
Stand in front of the mirror exposing the chest up to the waist, look at the breasts through the mirror, while keeping the arms in positions.
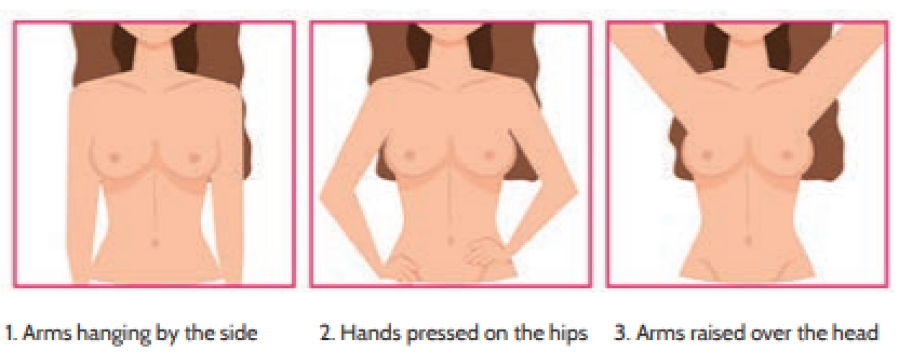
Note the changes mentioned below:
- Skin changes of the breasts
- Change in shape of the breasts
- Orange peel / Peau d’orange appearance of the breast
- Ulceration on the breast
- Late occurrence of breast asymmetry (most women may have asymmetry in normal circumstances. Therefore, a long- standing breast asymmetry is not a sign of a cancer)
- Nipple changes, discharges other than breast milk/ inverted nipple (having inverted nipples from birth is not a sign of a cancer)
- Breast lump, change in the texture, thickening of the breast skin.
- Lumps in the arm pit or around the neck
2. Palpation (Either lying down, sitting, standing)
Palpate the breast using middle three fingers to identify thickened areas and or lumps. Use the palmar surfaces of the fingers (flat surface of the three middle fingers). Palpation of breast can be done in sitting or lying down positions. On examining right breast, raise the right arm over the head and palpate the right breast using the left hand. While examining the left breast raise the left arm and palpate the left breast using the right hand.
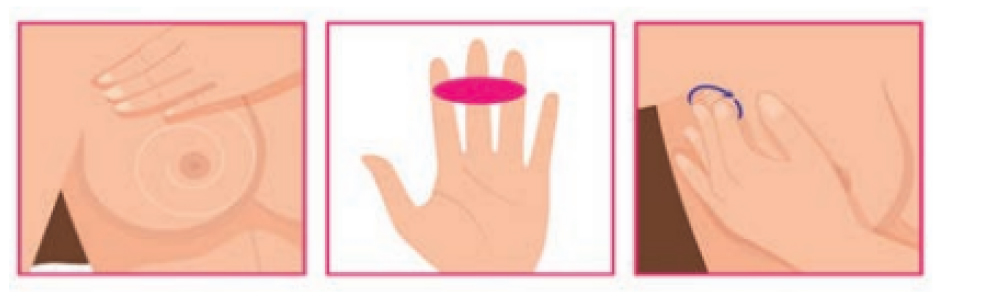
Continue palpating the breast in a clockwise direction from outer circle of the breast towards the nipple using three pressure levels.
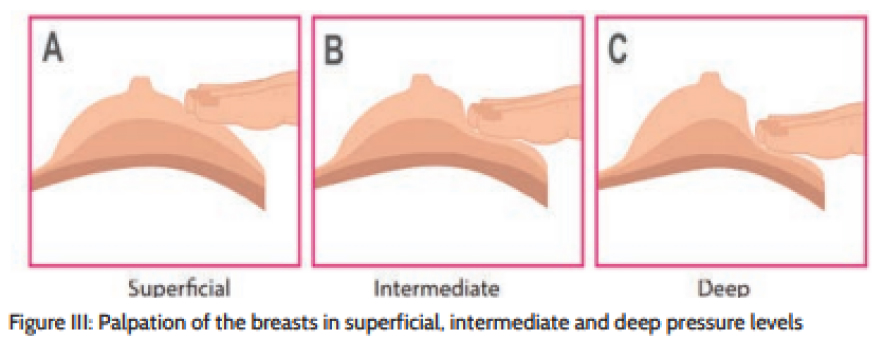
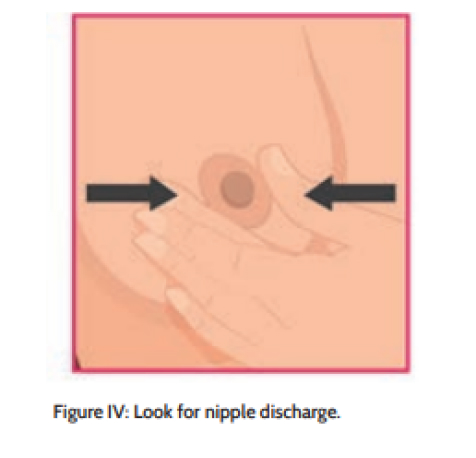
Start with applying ‘minimal’ pressure as indicted (to feel the area just beneath the skin) and then gradually increase the pressure (to feel the tissue deeper within). At the end of the breast palpation, find out whether there is a nipple discharge by squeezing the areola using thumb and middle finger.
![]()
Then examine the armpit and look for lumps. Use the same technique to examine the other breast.
Palpation of breast in lying down position:
To palpate the right breast, keep the right palm beneath the head and palpate the breast using the left hand. For the palpation of left breast, keep the left palm under the head and palpate with the right hand.
If any abnormality is detected during self-breast examination, it is necessary to consult a doctor even though all
the changes may not be due to breast cancer.
Contact FPA Sri Lanka on 077 955 2979 to book your screening appointment.
.png)


